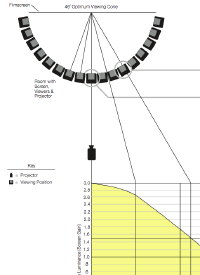
Two years ago, the evolution and rush to all things digital in the cinema world reached a classic chasm point, especially for digital cinema presentation to the theater screen. (See bottom question/answer.) It seemed that the technology was worked out, it seemed that the politics were worked out, it seemed that the financing models were worked out…and yet, the number of installations and new sales sat flat…or worse.
Huge companies like Texas Instruments (TI) and Sony had spent millions getting the technology ready for a secure and marketable implementation. Their OEM partners where ready to throw the handle to ‘Plaid’ to fill the needs of 125,000 screens in a world that needs to go from film-based to digital server based systems. The changeover requires a 60-80 thousand euro projector and 20,000 euro server to replace a 30,000€ film chain, a mature technology that typically lasted multiple decades with minor maintenance. But to the rescue, the studios offered plans that would pay back the initial investment by a mechanism known as a Virtual Print Fee (VPF). These were developed to compensate certain cinemas, over time, for playing inexpensive digital copies (distributed via hard disk and eventually satellite and fiber) instead of expensive film prints (distributed by trucks and airplanes.)
So, with all the ducks so apparently in a row, why weren’t the 7,000 ‘innovators’ and early adopters of 2007 joined by 10’s of thousands more screens by early 2010, when the number was merely double that (even after the initial 3D explosion)?
The reality was that the technical, political and financial realities weren’t really ready. Notwithstanding the world financial collapse that hindered access to the billions needed for the transition, there were nuances that made financing not so simple. In addition, the standards were still in transition, both on paper and in the labs and factories.
Financially, the major Hollywood studios are prepared to finance the transition up to the amount that they save in print costs and distribution. The nuance is that they only send out prints to the first-run cinemas, leaving the 2nd and 3rd level cinemas with no funding. (The background nuance is that once the digital transition is complete, the studios save billions per year forever, but are only helping to fund the initial roll-out. The exhibitors save a few low cost employees, and benefit from better quality and the ability to present features other than movies.)
World-wide, the Hollywood studios that developed the VPF mechanisms also didn’t find it fair that they should have to finance cinemas which made income from movies other than Hollywood movies. Nor did they want to overpay for equipment if a cinema made money from operas, concerts, sports or other alternative content that digital projection allows. This caused many national groups, in particular those in the UK, France, Italy and Germany to search for ways to fund the smallest to mid-sized facilities so that they would have digital equipment when enough critical mass was reached for film prints to become ancient history.
The UK funded several hundred screens with lottery money in one partially successful experiment, but it exposed a few holes in the plans. Simply stated, a movie’s life starts in one screen for a week or two, then moves to a smaller screen while the next movie in line attempts to take the larger audience in the larger room. But if there is only one set of digital gear, and that in the larger room, then the cinema still needs a film print to complete the movie’s run. One of the points of a Hollywood VPF is an agreement to get 50% of screens digital in one year and 100% in three years (with at least one capable of 3D.)
When the slow wheels of national finance plans got past the proposal stage, the largest cinemas in France and Germany complained that the ‘tax’ they paid per ticket was funding their competitors. Both plans were recently (in the last few months) thrown out as unfair by the country’s legal systems. (Norway figured it out on their own and are on their way to digitizing the entire country’s cinemas.
Meanwhile, the standards committees within the Society of Motion Pictures and Television Engineers (SMPTE) completed the last of the standards documents in 2009, submitting them to the ISO in the process. What should have been to no one’s surprise, some of the equipment, in particular the installed projectors that utilize the Texas Instruments chipset (the vast majority), didn’t meet those standards. In fact, the first projectors (dubbed ‘Series II’) to meet those standards were released in March 2010, at the industry’s ShoWest convention. Unlike the WiFi industry’s ability to ship equipment for over a year before the standards validated their presumed compliance, there are several pieces of older digital projection gear that will need expensive updating, with some equipment updatable and technically passing compliance requirements, but not able to include some important ‘modern’ features.
In addition to finally getting compliant projectors, those who waited for the new Series II equipment will also be getting equipment that is able to run with lower power consuming bulbs, and of course, give more light to the all important 3D image.
The invasion of 3D movies has been a boon to cinemas. The studios have all embraced it by announcing an ever increasing 3D release schedule, first with animated releases, but now (famously with the Avatar release) with CGI enhanced live action. The exhibitors not only are able to attract larger audiences with this nascent technology, but they are able to charge more per ticket in the process. This helped give the industry its first 10 billion dollar year in 2009, and keep actual ticket sales on an upward trend. In the alternative content area, live opera is still the most prevalent and successful, but live pop concerts have been successful, and more are slated. Sporting events have been experimented with, some in 3D, and will probably become more successful in the near future.
Coincidently, a few major installation groups have gotten financing in the last few months – It appears that the three largest US chains have the financing to cover 10 or 12 or 14,000 of their 17,000 screens. The disparity between PR and reality is not a trifle, but public information is hard to come by. The announcement that they were working with JPMorgan for money in 2007 mentioned numbers that were twice (Celluloid Junkie-More Rumblings About DCIP’s Financing) what they announced recently. And, the recent announcements don’t mention how they will finance 3D equipment, which costs up to $30,000 per screen…and is not covered by VPF agreements.
Notwithstanding those hidden nuances, it finally is movement across the chasm from innovators to more conservative early adopters. In addition, several integrators in Europe, India, China, Japan and Korea have recently announced hundred and multi-hundred piece installation deals in their areas. See: DCinemaToday for up to the minute market news for the exhibition side of digital cinema.
With the release of the Series II equipment, other features that were built into the standards are driving manufacturers to build matching equipment. Most welcome is equipment for the deaf/hard of hearing and visually impaired communities (HI/VI). There was a special exhibition at ShoWest of these company’s works-in-progress; devices that use special glasses that create closed captions which float the text over the screen (so that one doesn’t have to constantly look up and down to see both), and another system that will use WiFi to put captions on one’s iPhone (among other devices), as well as new ways to put dialog-enhanced audio into earphones.
The best news for the HI/VI field is that the SMPTE and ISO standards are are in place, have been recently ‘plug-fest’ tested for interoperability, and contrary to the previous film-centric systems, the new standards are based upon open, not proprietary (read: patented, licensable, expensive, frustrating) technology. (For a brief discussion on HI/VI captioning and the `enthusiasm’ of differing viewpoints, see: Smashing Down The Door – Digital Cinema and Captions For the Deaf and Hard of Hearing)
The arguments still persist around the excellent qualities of film, much like the arguments in the audio world about the qualities of tape recording and vinyl. While some of the arguments are interesting and some of those even true (the ability/inability to wash a screen with the indescribable transitions of Lawrence of Arabia‘s desert sunset comes to mind), the arguments against film are too many. Film is an ecological nightmare, the prints are expensive to ship around, re-gather and store, and whatever qualities that they exhibit at first runs are grossly diminished after a week of getting banged around within the film projection process. And unlike the audio business, where specialty houses can still afford to make tape for those who want to record on it, as fewer companies use film for shooting and exhibition, the cost of material and processing will become too expensive for the budgets of even the Spielberg’s of the art.
Fortunately, the evolution of quality in digital production and post-production equipment has substantially gone beyond the requirements of ‘film’ makers. As with all recent digital technology, quality points are also being hit at the low end, so that artists can make motion pictures which can fill the big screen for less money and take advantage of the substantial distribution benefits of the digital infrastructure. At the high end, artists can do more, perhaps more quickly and certainly with more flexibility and features. For the consumer, this means that quality is possible from a wider range of storytellers and the possibility to see material from other regions around the world becomes more easily accomplished.
Part II of this series goes into more detail on specifications, some current realities of 3D technology, what “substantially gone beyond the requirements” really means, and a brief excursion on how it relates to the home market.
References:
DCinemaToday
MKPE’s Digital Cinema Technology FAQ
This Series now includes:
The State of Digital Cinema – April 2010 – Part 0
The State of Digital Cinema – April 2010 – Part I
The State of Digital Cinema – April 2010 – Part II
Ebert FUDs 3D and Digital Cinema